Understanding REEVs: The Next Generation of Hybrid Vehicle Technology
As the global automotive industry transitions toward sustainable mobility, Range-Extended Electric Vehicles (REEVs) have emerged as a pivotal bridge between traditional internal combustion engines (ICE) and full battery electric vehicles (BEVs). REEVs—also known as REX (Range Extender) hybrids—blend the advantages of electric propulsion with the security of extended driving range, all while offering reduced emissions and optimized fuel efficiency.
What Makes a REEV Different?
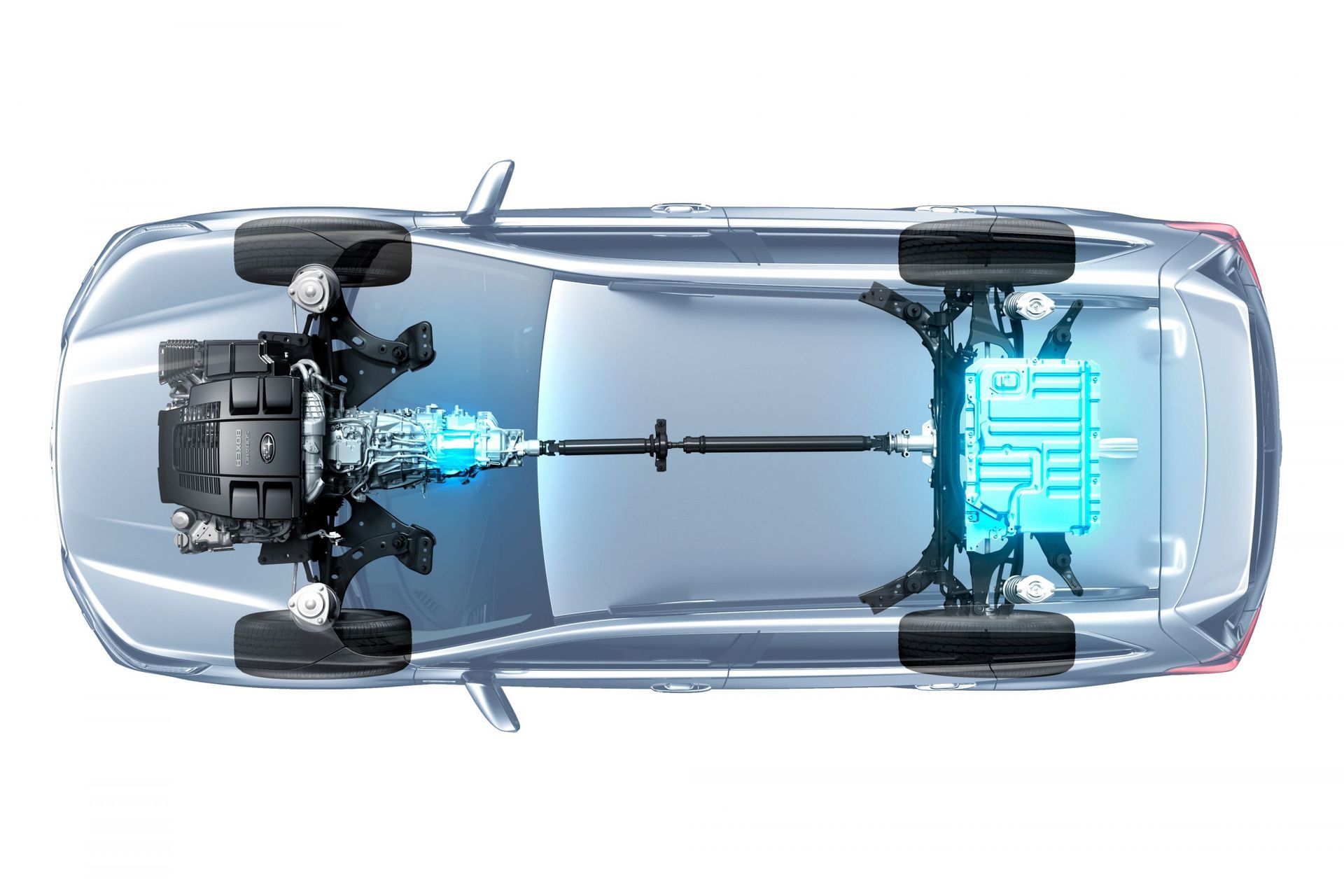
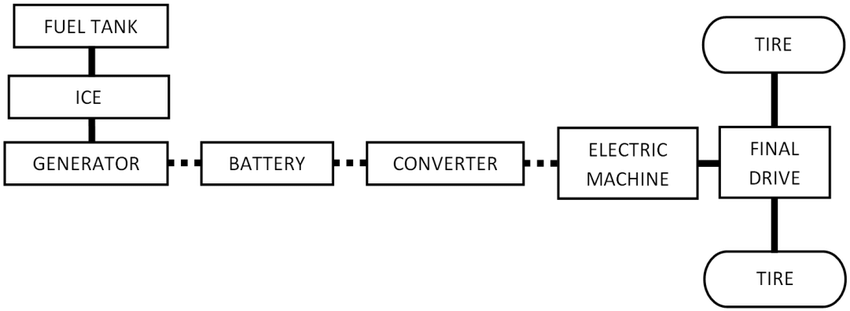
At the core of a REEV is a fundamental departure from conventional hybrid powertrains. In traditional hybrids, such as those seen in Toyota’s Prius or Honda’s Insight, both the electric motor and internal combustion engine (ICE) contribute directly to propulsion. A REEV, however, takes a different route:
- Primary Drive Source: An electric motor is the sole propulsion unit.
- ICE Role: A small petrol engine operates only as an onboard generator to recharge the battery or provide power to the electric motor indirectly via an electric generator system.
- No mechanical connection between the ICE and the drivetrain (in most cases).
This architecture is known as a series hybrid configuration, in contrast to the parallel hybrid layout of traditional hybrids.
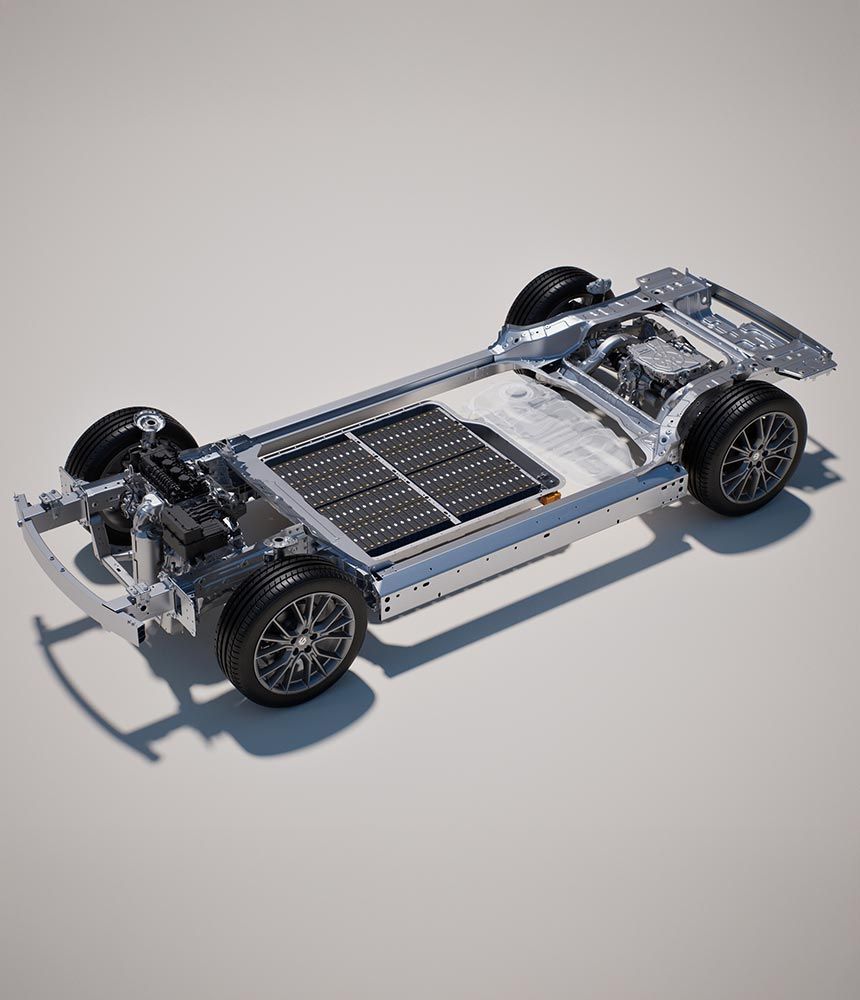
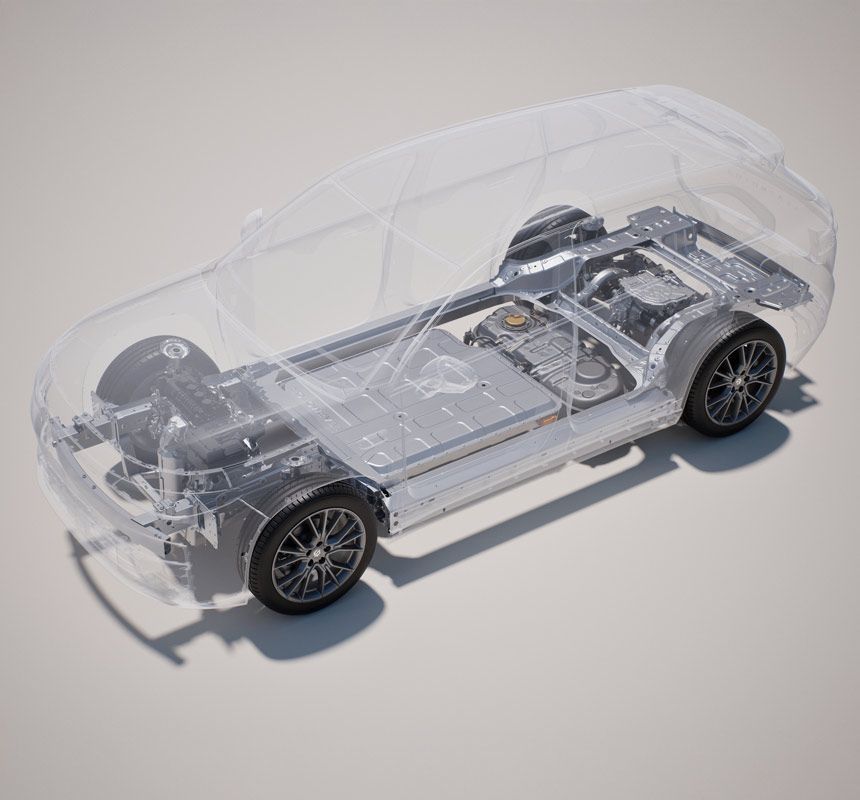
Technical Breakdown: Components and Operation
A typical REEV system consists of:
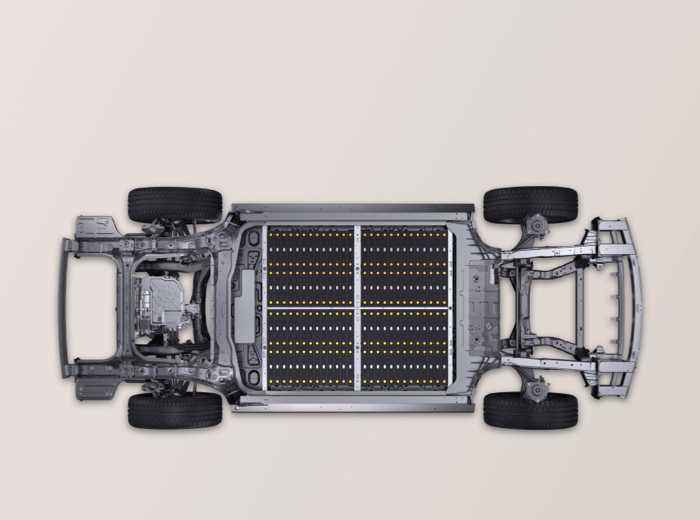
- High-capacity lithium-ion battery pack: Stores electrical energy and supplies it to the traction motor.
- Electric traction motor: Provides all torque to the wheels.
- ICE-powered generator: Converts gasoline into electricity when the battery state-of-charge (SOC) drops below a set threshold.
- Power electronics module: Manages energy flow between the battery, motor, and generator.
- Regenerative braking system: Captures kinetic energy during braking and stores it in the battery.
Driving Modes
- EV Mode (All-Electric): Vehicle runs solely on battery power; ideal for short trips and urban driving.
- Range-Extender Mode: When battery drops below a set SOC (typically ~20-30%), the ICE kicks in to generate electricity to power the motor or recharge the battery.
- Charge-Sustaining Mode: ICE maintains the battery at a minimal charge state to ensure continued EV operation.
Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Because the ICE operates at a constant and optimized RPM, fuel efficiency is typically higher than in conventional vehicles where the engine's RPM fluctuates. The result is:
- Lower fuel consumption
- Reduced tailpipe emissions
- Decreased wear and tear on mechanical components due to the absence of a traditional transmission
Many REEVs meet stringent emissions standards such as Euro 6 and California's SULEV (Super Ultra-Low Emission Vehicle) standards, making them a compelling option in eco-conscious markets.
REEVs vs. BEVs and PHEVs
| Feature | REEV | BEV | PHEV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary propulsion | Electric motor | Electric motor | Both ICE & electric motor |
| Range-extending ICE | Yes (generator only) | No | Yes (drives wheels) |
| EV range | Moderate (80-150 km) | High (300-600+ km) | Low to Moderate (30-80 km) |
| Charging | Plug-in + ICE charge | Plug-in only | Plug-in + ICE |
| Ideal for | Long trips + urban use | Urban + daily commutes | Mixed driving needs |
REEVs bridge the gap between PHEVs (Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles) and BEVs. Unlike PHEVs, the ICE in a REEV doesn’t drive the wheels, simplifying drivetrain complexity and improving long-term reliability.
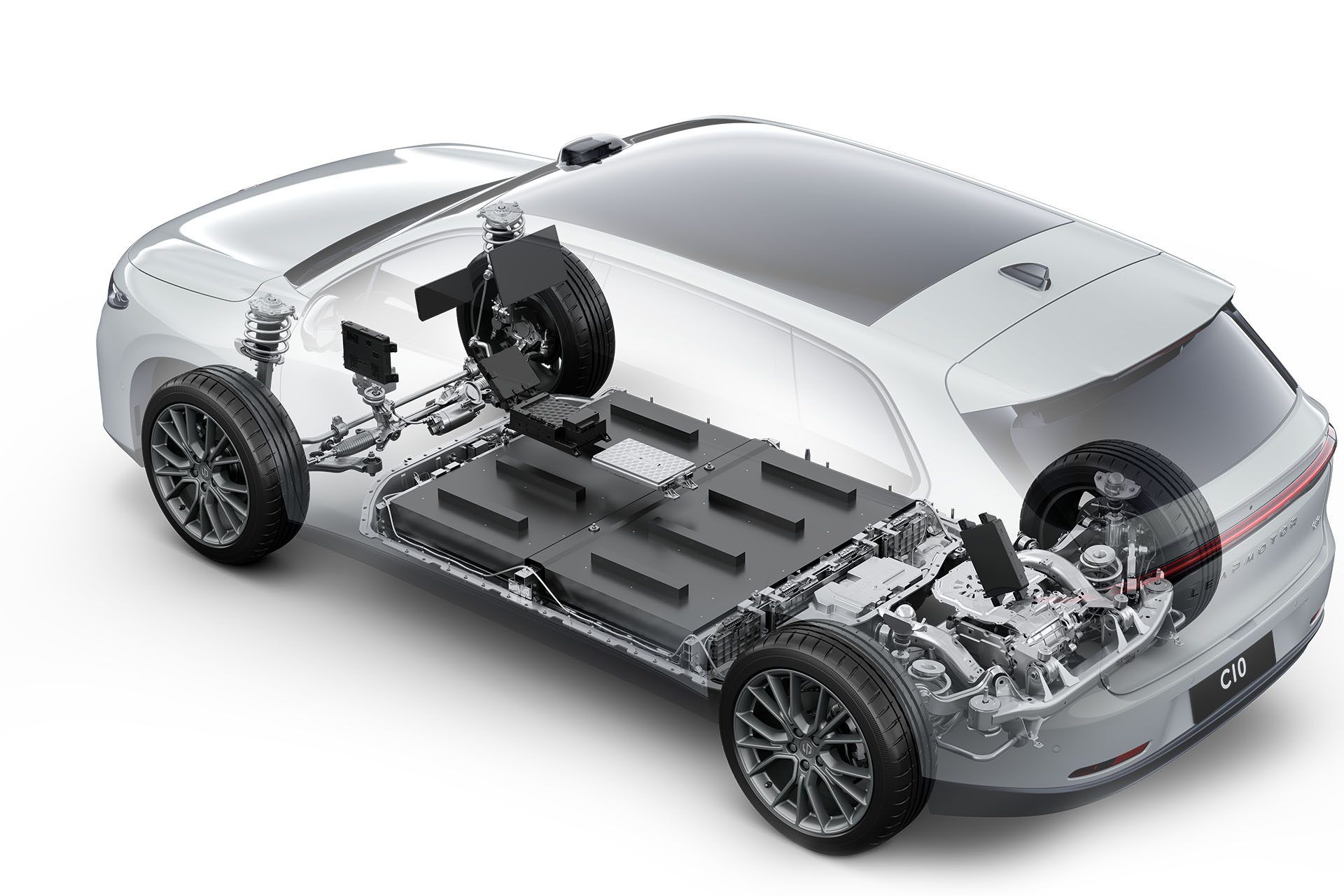
Leapmotor C10 REEV Ultra Hybrid – Electric Power without Limits
The C10 REEV Ultra Hybrid is a revolutionary medium SUV that blurs the lines between traditional and electric vehicles.
Featuring the advanced Range-Extender Electric Vehicle (REEV) technology, the C10 offers an unmatched combination of efficiency, power, and flexibility. Drivers can experience full electric driving without worrying about range.
The C10 REEV Ultra Hybrid is equipped with a petrol engine that continuously charges the battery.
Current and Emerging REEV Models
Several automakers have invested in REEV technology. Notable examples include:
- BMW i3 REx: One of the first widely recognized REEVs; features a two-cylinder petrol engine that generates electricity.
- Mazda MX-30 e-Skyactiv R-EV: A new entrant using a rotary engine as a generator, showcasing Mazda’s commitment to compact and efficient ICE tech.
- Volvo and GM: Exploring range extenders as transitional tech for future electric fleets.
As battery technology improves, the EV range of REEVs will increase, further reducing the need to rely on the ICE.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
- Cost: REEVs require both a high-voltage battery and an ICE generator, which can make them more expensive to produce.
- Packaging complexity: Balancing battery size, fuel tank capacity, and ICE generator location requires precise engineering.
- Market confusion: Consumers often confuse REEVs with hybrids or PHEVs, leading to unclear expectations.
Opportunities
- Fleet integration: Ideal for commercial applications requiring long operational hours with reduced emissions.
- Rural areas: Perfect for regions with limited charging infrastructure.
- Transition vehicle: Acts as a stepping stone for users reluctant to adopt full BEVs due to range anxiety.
Future Outlook
As global regulations push for net-zero emissions and full electrification, REEVs provide a scalable and sustainable transitional technology. With rising investments in compact, high-efficiency range extenders (including microturbines and rotary engines), REEVs may continue to gain popularity in both consumer and fleet markets.
Moreover, as solid-state batteries and renewable fuels evolve, the potential synergy between clean power generation and electric propulsion in REEVs could redefine their role beyond mere transitional tech.
Conclusion
Range-Extended Electric Vehicles represent a compelling blend of electric efficiency and combustion reliability. By decoupling the engine from the drivetrain, REEVs achieve a smart balance of range, performance, and sustainability. While BEVs may dominate the long-term future, REEVs are poised to play a crucial role in the present-day shift toward cleaner, smarter mobility.