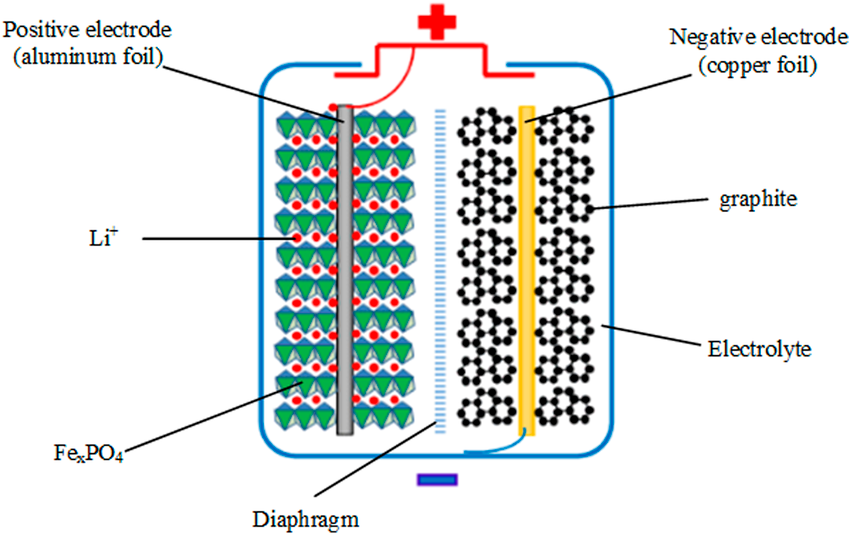
Silicon Carbide Semiconductors: The Next Evolution in Toyota’s Hybrid Powertrains
For decades, Toyota’s hybrid systems have relied on traditional silicon semiconductors to control power flow between the battery, electric motor, and internal combustion engine. However, Toyota is now transitioning to silicon carbide (SiC) semiconductors, which are poised to deliver more power while reducing energy loss.
What Makes Silicon Carbide Superior?
Silicon carbide semiconductors offer several advantages over conventional silicon-based chips:
- Higher Efficiency – SiC semiconductors minimize energy loss and generate less heat, improving overall system efficiency.
- More Power with Less Fuel – By optimizing power transfer, SiC chips enhance acceleration and reduce fuel consumption.
- Better Performance in Harsh Conditions – These semiconductors are more durable and function efficiently at higher temperatures, making them perfect for hybrid vehicles operating in diverse environments.
- Increased Battery Lifespan – SiC technology reduces strain on the battery, extending its durability and effectiveness.
Toyota’s move toward SiC technology will further enhance the fuel economy of its hybrid models, making them even more appealing to consumers looking for low-emission, high-efficiency vehicles.